Strengthening Dependency Security: Best Practices for Vulnerability Scanning, Automatic Updates, and OSS License Management
This post is also available in .
Introduction
In recent years, the use of OSS (open-source software) has expanded rapidly and has become indispensable for improving development efficiency. However, it is also true that incorporating external libraries introduces risks such as vulnerabilities and license violations.
In particular, leaving packages that contain vulnerabilities unattended can threaten the security of the entire project, so proper management is required.
This article focuses on the following points and explains how to improve the security of your project:
- Introducing automatic scanning with Snyk / Dependabot (regular vulnerability checks)
- Identifying vulnerabilities in existing packages and proposing updates
- Designing an appropriate version management strategy for libraries in use
- Setting up alert notifications for packages containing critical vulnerabilities (Slack / Teams integration)
- Using npm audit / yarn audit / pnpm audit and creating reports
- Reducing unnecessary package dependencies to lower attack risk
- Proper management of OSS licenses (checking for license violations)
- Checking EOL (End of Life) for libraries used in existing projects
- Defining security evaluation criteria for newly introduced packages
1. Introducing Automatic Scanning with Snyk / Dependabot
Snyk and Dependabot are tools that automatically detect and fix vulnerabilities in dependencies. By using these tools, you can improve application security and minimize the impact of vulnerabilities.
Introducing and Using Snyk
Snyk is a SaaS-based security tool that scans for vulnerabilities in dependencies and proposes fixes. By integrating it with GitHub, GitLab, etc., you can automatically create pull requests for fixes and greatly reduce the time required for remediation.
Steps
- Create a Snyk account and integrate it with GitHub / GitLab / Bitbucket, etc.
- Scan the repository and detect vulnerabilities in existing dependencies
- Use
snyk monitorto run scans regularly - Integrate with CI/CD to automatically run scans at build time
Example) Add to GitHub Actions
name: Snyk Security Scan
on: push
jobs:
security:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Run Snyk Test
uses: snyk/actions/node@master
env:
SNYK_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SNYK_TOKEN }}
Steps to Introduce Dependabot
- Basic Dependabot features (enable from the GitHub settings screen)
This is provided as “Security updates” and can be easily enabled from the GitHub repository settings.
- Go to the GitHub repository
- Settings → Security → Code security and analysis
- Enable "Dependabot security updates" ✅
- This integrates with GitHub Security Advisories, and when a critical vulnerability is found in existing dependencies, a PR is automatically created.
- Detailed update management using Dependabot’s dependabot.yml
Security updates alone are not suitable for the use case of “automatically updating when a new version is released.” By using .github/dependabot.yml, you can regularly check dependencies and create PRs even when there are no vulnerabilities.
version: 2
updates:
- package-ecosystem: "npm" # For npm (also supports yarn, pip, maven, etc.)
directory: "/" # Root directory
schedule:
interval: "weekly" # Check weekly (daily, monthly also possible)
open-pull-requests-limit: 5 # Open up to 5 PRs
2. Identifying Vulnerabilities in Existing Packages and Proposing Updates
Vulnerability scanning for dependencies in a repository can be automated using tools such as Snyk and Dependabot. This allows you to obtain the following information and quickly proceed with vulnerability remediation:
- How scanning works
Snyk and Dependabot analyze package.json and yarn.lock (or package-lock.json) in the repository and check the versions of the libraries you depend on.
These tools compare against vulnerability databases (CVE, GitHub Advisory Database, etc.) and provide information such as:
- Known vulnerabilities in dependent packages
- Affected files or modules
- Severity: Low / Medium / High / Critical
- Recommended versions that fix the issue
- Scope of impact (direct dependency / transitive dependency)
- Response flow for the development team
Running scans
-
Regularly check snyk test and GitHub Dependabot Alerts
- Integrate scans into the CI/CD pipeline
-
Check the scope of impact
- Confirm whether it is a direct dependency or a dependency via another library
- Prioritize items with Critical / High severity
-
Perform updates
- If possible, update to the recommended version (yarn upgrade / npm update, etc.)
- Test for compatibility issues
- Apply changes to the release
-
Continue monitoring
- Continue regular scans (integrated into CI/CD)
- Watch vulnerability information (Snyk and GitHub Security Advisories)
Designing an Appropriate Version Management Strategy for Libraries in Use
An appropriate version management strategy for libraries is essential to maintaining project stability and security. The following points are explained in detail.
- Understanding and applying Semantic Versioning (SemVer)
Semantic Versioning (SemVer) is a common rule for library version management. Applying it properly helps minimize the impact of updates.
- Managed in the format MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
- MAJOR: Increased when there are breaking (incompatible) changes
- MINOR: Increased when new features are added in a backward-compatible way
- PATCH: Increased for bug fixes (fixes to existing functionality only)
- Consider the impact of updates
^1.2.3(caret): Updatable within the 1.x.x range (will not update to 2.0.0)~1.2.3(tilde): Updatable within the 1.2.x range (will not update to 1.3.0)- 1.2.3 (exact): Use only the specified version
- Operational examples
- Carefully consider MAJOR version upgrades when updating libraries
- Use
^for dependencies and~for devDependencies in package.json to reduce changes in the development environment
- Use lock files (
package-lock.json/yarn.lock)
By using lock files, you can achieve consistent version management when installing in different environments.
package-lock.json(npm) /yarn.lock(Yarn) record the exact versions of each dependency- In team development, commit the lock file to Git to maintain unified versions
Operational examples
- In CI/CD environments, use
npm cioryarn install --frozen-lockfileto reproduce fixed versions - During review, check that the lock file does not contain unintended changes
- Regular update checks
If you neglect library updates, security vulnerabilities and bugs may affect your project. Regular update checks are important.
Automatic checks using tools
- Dependabot (GitHub): Automatically detects updates to package.json and creates pull requests
- Snyk: Scans vulnerabilities in dependent libraries and proposes countermeasures
- Understand changelogs
Library updates may introduce API specification changes or incompatibilities. Get into the habit of checking the changelog before updating.
- Check CHANGELOG.md / GitHub Releases / npm release notes
- Pay particular attention to major version upgrades (check the impact of breaking changes)
- Be cautious with versions tagged as canary or beta
Operational examples
- Test large updates in a separate branch and verify compatibility
- For updates with a large impact, check issues and documentation in advance and apply them in stages
Setting Alert Notifications for Packages Containing Critical Vulnerabilities (Slack / Teams Integration)
To enable immediate response when vulnerabilities are detected, configure notifications to Slack or Microsoft Teams.
Setting Slack notifications in Snyk
- From the Snyk dashboard, go to Integrations
- Select Slack and connect your workspace
- Configure notification triggers (e.g., High / Critical vulnerabilities)
- Confirm that notifications are sent to the specified channel
Notifications via GitHub Actions for Dependabot
- Set
assigneesandreviewersindependabot.yml - Configure a
GitHub Actionsworkflow with theon: pull_requesttrigger - Use
slack-notify-actionto send a notification when a PR is created
This improves the speed from vulnerability discovery to remediation.
Using npm audit / yarn audit / pnpm audit and Creating Reports
How to use npm audit
npm audit analyzes package-lock.json and checks for known security issues.
npm audit
When you run this command, it lists affected packages, vulnerability severity (low, moderate, high, critical), scope of impact, and possible remediation methods.
Automatically fixing vulnerabilities
- Apply only low-impact updates (compatible updates only)
npm audit fix
- Force major version upgrades (risky but suitable for immediate resolution)
npm audit fix --force
By running npm audit in your CI/CD pipeline, you can perform continuous security audits.
npm audit --json > audit-report.json
You can parse this JSON report and build a mechanism to raise alerts when security issues occur.
How to use yarn audit
- Basic usage
If you are using Yarn, it audits dependencies based on yarn.lock.
yarn audit
- Outputting a JSON report
Yarn can also output audit results in JSON format for use in CI/CD.
yarn audit --json > audit-report.json
- Failing on issues above a certain severity
You can fail the process when vulnerabilities of a specified level (low / moderate / high / critical) or higher are detected.
yarn audit --level critical
How to use pnpm audit
- Basic usage
pnpm auditalso performs security checks on dependencies, similar to npm and yarn.
pnpm audit
- Outputting a JSON report
You can use this when you want to save and monitor audit results in CI/CD.
pnpm audit --json > audit-report.json
- Failing the process in CI/CD
You can use error handling to fail the build when specific vulnerabilities are detected.
pnpm audit --json > audit-report.json || exit 1
Example of automatic auditing in CI/CD
Here is how to use GitHub Actions to run npm audit regularly and send alerts when vulnerabilities are detected.
name: Security Audit
on:
schedule:
- cron: '0 0 * * *' # Run every day at 00:00
jobs:
security-audit:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Run npm audit
run: npm audit --json > audit-report.json || exit 1
- name: Upload audit report
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: audit-report
path: audit-report.json
In this configuration, npm audit runs daily, and the GitHub Actions job is set to fail when vulnerabilities are present.
Reducing Unnecessary Dependencies and Lowering Attack Risk
Dependency management is extremely important both from a security perspective and from a project maintenance perspective. Removing unnecessary dependencies provides the following benefits:
Risks of unnecessary dependencies
- Security risks
- Dependent packages may contain vulnerabilities
- The deeper the dependency tree, the higher the chance of including vulnerable versions
- There is a risk of supply chain attacks (e.g., developer account hijacking) introducing malicious code
- Increased management costs
- Package updates and maintenance become more complex
- An increase in unused packages can negatively affect build time and application performance
- Dependency conflicts are more likely, increasing debugging costs
How to identify unnecessary dependencies
depcheck is a tool that can identify dependencies that are actually not used in the project.
npx depcheck
When run, it detects the following:
- Unused dependencies (unused in dependencies)
- Unused devDependencies (unused in devDependencies)
- Missing dependencies (dependencies not found)
To manually remove unnecessary dependencies:
npm uninstall <package>
or
yarn remove <package>
Optimizing dependencies
You can optimize the package structure by consolidating duplicate packages.
npm dedupe
Proper Management of OSS Licenses
Proper management of OSS (open-source software) licenses is important for safely using OSS in commercial projects while avoiding legal risks. Details are as follows.
Importance of OSS license management
When using OSS in commercial projects, you need to check the following points:
- License compatibility
- Whether the license is allowed for use in your project (e.g., MIT and Apache-2.0 allow commercial use, while GPL-3.0 has strong restrictions)
- Obligations required by each license (e.g., credit display, obligation to disclose source code)
- Avoiding license violation risks
- Violating OSS licenses may result in legal action
- GPL (GNU General Public License) in particular requires source code disclosure, so it needs special attention
- Tracking license changes and updates
- Licenses may change when OSS is updated
- Regular audits are required
Using npm-license-crawler
npm-license-crawler is a tool that retrieves license information for all packages in node_modules and outputs it in CSV or JSON format.
It has the following characteristics:
- Fewer deprecation warnings about dependencies than
license-checker - Easy to output results in JSON or CSV format
- Can filter by specified licenses
- Suitable for license audits in CI/CD
Display licenses for all packages
npx npm-license-crawler
Example (output image):
└─ zod@3.23.8
├─ licenses: MIT
├─ repository: https://github.com/colinhacks/zod
├─ licenseUrl: https://github.com/colinhacks/zod/raw/master/LICENSE
└─ parents: exapmle
Get license information in JSON format
npx npm-license-crawler --json licenses.json
Example (output image):
"zod@3.23.8": {
"licenses": "MIT",
"repository": "https://github.com/colinhacks/zod",
"licenseUrl": "https://github.com/colinhacks/zod/raw/master/LICENSE",
"parents": "example"
}
Get license information in CSV format
npx npm-license-crawler --csv licenses.csv
Example (output image):
"zod@3.23.8","MIT","https://github.com/colinhacks/zod","https://github.com/colinhacks/zod/raw/master/LICENSE","example"
Checking EOL (End of Life) for Existing Libraries
What is EOL (End of Life)?
EOL (End of Life) refers to the end of development and support for software or libraries. Libraries that have reached EOL carry the following risks:
- Security risk: newly discovered vulnerabilities will not be fixed
- Compatibility issues: may become incompatible with newer versions of Node.js or other libraries
- No more feature additions: no new features or optimization updates
Check current and latest versions of packages in the project
This command lets you check the current and latest versions of packages in your project.
npm outdated
Example output
Package Current Wanted Latest Location
@hookform/resolvers 3.9.0 3.10.0 4.1.3 node_modules/@hookform/resolvers
@types/react 18.3.11 18.3.18 19.0.10 node_modules/@types/react
@types/react-dom 18.3.1 18.3.5 19.0.4 node_modules/@types/react-dom
class-variance-authority 0.7.0 0.7.1 0.7.1 node_modules/class-variance-authority
eslint 8.57.1 8.57.1 9.21.0 node_modules/eslint
eslint-config-prettier 9.1.0 9.1.0 10.0.2 node_modules/eslint-config-prettier
eslint-plugin-prettier 5.2.1 5.2.3 5.2.3 node_modules/eslint-plugin-prettier
eslint-plugin-tailwindcss 3.17.5 3.18.0 3.18.0 node_modules/eslint-plugin-tailwindcss
postcss 8.4.47 8.5.3 8.5.3 node_modules/postcss
prettier-plugin-tailwindcss 0.6.8 0.6.11 0.6.11 node_modules/prettier-plugin-tailwindcss
react 18.3.1 18.3.1 19.0.0 node_modules/react
react-dom 18.3.1 18.3.1 19.0.0 node_modules/react-dom
react-hook-form 7.53.1 7.54.2 7.54.2 node_modules/react-hook-form
tailwind-merge 2.5.4 2.6.0 3.0.2 node_modules/tailwind-merge
tailwindcss 3.4.14 3.4.17 4.0.9 node_modules/tailwindcss
typescript 5.4.3 5.4.3 5.8.2 node_modules/typescript
zod 3.23.8 3.24.2 3.24.2 node_modules/zod
Meaning of each column
- Current (currently installed version)
- Wanted (latest version installable within the range in package.json)
- Latest (latest version available in the registry)
When you see results like the above, you need to take actions such as the following:
-
Minor version updates
- Run
npm update(automatically updates up to the Wanted version) - Since the likelihood of breaking changes is low, it is generally safe to apply
- Run
-
Major version updates (with caution)
react,react-dom, andtailwindcsshave major updates, so check the changes- Investigate the scope of impact, and if you decide to update, run
npx npm-check-updates -uto updatepackage.json, thennpm install
How to check if something is EOL
npm outdated and npm-check-updates alone cannot determine whether a library is EOL. Use a combination of the following methods:
- Check official documentation and release notes
Check the library’s official site or GitHub release notes for any “EOL” announcements.
Example: React release notes
Example: Node.js EOL schedule
- Check activity on the GitHub repository
You can check whether it is being maintained by looking at the commit history and issues on GitHub.
- Last commit was more than a year ago
- Issues are left unresolved
- There is a note such as “This project is no longer maintained”
If you see such signs, the library is likely EOL.
- Use npm trends or Libraries.io for investigation
You can also use tools that show library trends and update frequency.
- npm trends (compare package popularity)
- Libraries.io (check EOL and update frequency)
What to do with EOL libraries
Consider the following measures when you find a library that has reached EOL.
- Check for recommended libraries
If an official replacement library is recommended, consider migrating to that library.
Example)
moment.js (EOL) → date-fns or luxon
-
Look for a maintained fork
For popular libraries, there may be maintained forks. Check the GitHub repository for active forks. -
If you absolutely cannot update
Usenpm auditto identify the impact of vulnerabilities and apply manual patches if necessary
Usepackage-lock.jsonto pin problematic versions and limit the scope of impact
Defining Security Evaluation Criteria for Newly Introduced Packages
When introducing new OSS packages, considering the following points can improve safety.
Maintenance status
To ensure the security and quality of an OSS package, it is important that it is properly maintained. Checking the following points helps you decide whether you can use it with confidence.
- Last updated date
- Check the last commit in the GitHub repository.
- If it has not been updated for more than a year, maintenance may have stopped.
- Status of issues and pull requests
- Check the Issues tab to see if critical bugs are left unresolved.
- Check the merge speed of pull requests to see if development is active.
- Activity of maintainers
- Check whether core developers are committing regularly.
- If major maintainers have left, see whether new developers have taken over.
Download count
Packages with many users are more likely to have been thoroughly vetted by the community and may be relatively safe.
-
npm trends- With
npm trends, you can compare the popularity of multiple packages. - Compare with competing packages to make an appropriate choice.
- With
-
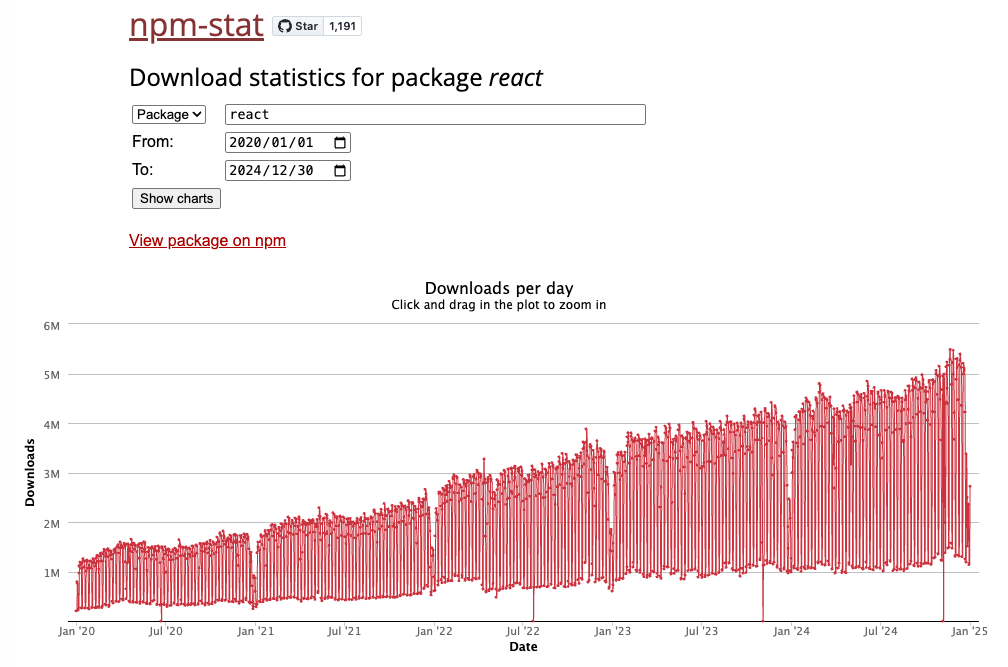
npm-stat
- Use npm-stat to check download counts over a specific period.
- Also check that there has not been a sudden drop in downloads.
Example) Download trend for React from 2020 to 2024.
Downloads are steadily increasing, so it can be considered a healthy package.
Known vulnerabilities
Before introducing a package, run a security scan to check for known vulnerabilities.
npm audit- GitHub Dependabot
- Snyk
Conclusion
When using OSS packages, it is not enough to simply install them; continuous security checks and proper management are essential.
By adopting the automatic scanning with Snyk / Dependabot and the use of npm audit / yarn audit introduced here, you can prevent vulnerabilities in advance and maintain a secure development environment.
In addition, thorough EOL checks and license management for libraries are also important points.
Introducing regular audits and alert notification mechanisms and raising security awareness across the team will lead to long-term stable operations.
To achieve a secure development environment, start implementing the measures you can apply right away.
Questions about this article 📝
If you have any questions or feedback about the content, please feel free to contact us.Go to inquiry form
Related Articles
Complete Guide to Web Accessibility: From Automated Testing with Lighthouse / axe and Defining WCAG Criteria to Keyboard Operation and Screen Reader Support
2023/11/21Introduction to Automating Development Work: A Complete Guide to ETL (Python), Bots (Slack/Discord), CI/CD (GitHub Actions), and Monitoring (Sentry/Datadog)
2024/02/12CI/CD Strategies to Accelerate and Automate Your Development Flow: Leveraging Caching, Parallel Execution, and AI Reviews
2024/03/12Bringing a Go + Gin App Up to Production Quality: From Configuration and Structure to CI
2023/12/06ESLint / Prettier Introduction Guide: Thorough Explanation from Husky, CI/CD Integration, to Visualizing Code Quality
2024/02/12Complete Guide to Implementing GitHub and Google OAuth Authentication with Next.js — How to Achieve Smooth User Login
2024/03/01Frontend Test Automation Strategy: Optimizing Unit, E2E, and API Tests with Jest, Playwright, and MSW
2024/01/21GraphQL × TypeScript × Zod: Type-safe API Development and Schema Management Using Code Generator
2024/02/12