ESLint / Prettier Introduction Guide: Thorough Explanation from Husky, CI/CD Integration, to Visualizing Code Quality
This post is also available in .
Introduction
To standardize code quality within a development team, a linter (ESLint) and a formatter (Prettier) are indispensable. A linter detects syntax and style issues in code, and a formatter unifies code formatting. This article explains the following initiatives in detail.
- Define ESLint rules that match your development team’s coding style and configure the project optimally
- Introduce Prettier to automatically unify code formatting
- Use Git hooks to automatically run ESLint and Prettier before commits
- Automatically fix code style issues
- Create documentation for configuration and usage
- Use Husky to standardize commit message formats
- Integrate Lint and Prettier into the CI/CD pipeline
- Visualize code quality as reports and build a mechanism for the entire team to track quality improvement progress
This article introduces concrete steps from how to introduce and configure ESLint and Prettier to automatically applying them using Git Hooks.
Why introducing a Linter / Formatter is important
In software development, maintaining consistency and quality of code is important. Especially in team development, if each developer has a different coding style, reviews and maintenance become difficult.
By introducing a linter (static analysis tool for code) and a formatter (code formatting tool), you gain the following benefits:
- Maintain code consistency and improve readability
- Enforce adherence to coding conventions to ensure quality
- Enable early detection of errors and bugs
- Reduce the burden of code reviews and allow focus on more essential discussions
Introducing ESLint and configuring it optimally for your project
ESLint is a linter that statically analyzes JavaScript and TypeScript code to improve code quality and consistency.
Features of ESLint
- Improve code quality: Detect syntax errors and potential bugs in advance
- Unify coding style: Apply a unified style across the team
- Customizable: You can define your own rules
- Plugin support: Can be extended for React, TypeScript, Prettier, etc.
- Auto-fix feature: Some issues can be automatically fixed with eslint --fix
Concrete rule examples
ESLint has many rules, including the following:
| Rule name | Description |
|---|---|
no-unused-vars |
Disallow unused variables |
no-undef |
Disallow use of undefined variables |
prefer-const |
Use const for variables that are not reassigned |
eqeqeq |
Use === instead of == |
semi |
Enforce semicolons |
quotes |
Unify to single or double quotes |
arrow-body-style |
Omit unnecessary {} |
object-curly-spacing |
Require spaces inside object {} |
react/jsx-uses-react |
Import React when using JSX |
react/prop-types |
Enforce use of PropTypes (disable if using TS) |
no-console |
Disallow console.log |
curly |
Require {} for control structures |
no-multiple-empty-lines |
Limit the maximum number of consecutive blank lines |
Installing ESLint
First, introduce ESLint into your project.
npm install --save-dev eslint
Or, if you use Yarn:
yarn add -D eslint
Initial setup
To initialize ESLint configuration, run the following command:
npx eslint --init
Select the following items interactively:
- How do you want to use ESLint? →
To check syntax and find problems - Which JavaScript environments does your project use? → Select
BrowserorNode.js - Which framework does your project use? → Select what you need such as
React - What format do you want your config file to be in? →
JSONorJavaScript
After configuration is complete, .eslintrc.json or .eslintrc.js will be created in your project.
Customizing rules
Edit .eslintrc.js to match your development team’s coding style.
module.exports = {
env: {
browser: true,
es2021: true,
},
extends: ["eslint:recommended", "plugin:react/recommended"],
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 12,
sourceType: "module",
},
rules: {
"indent": ["error", 2],
"quotes": ["error", "single"],
"semi": ["error", "always"],
},
};
extends: Apply recommended rule setsrules: Add custom rulesplugins: Add support for React or TypeScript
Gradually increasing the number of rules is, in my opinion, the key to using ESLint over the long term.
Introducing and configuring Prettier
Prettier is a code formatter that automatically formats code such as JavaScript and TypeScript.
Features
- Unify code style: You can standardize how code is written within the team.
- Automatic formatting: Automatically adjusts indentation and spacing.
- No need for manual fine-tuning: Since it applies a consistent format according to rules, developers don’t need to worry about minor style details.
- Editor integration: Can auto-format on save in editors like VS Code.
- Can be used together with ESLint: You can combine it with static analysis (bug checking) in addition to code style.
Supported languages
- JavaScript, TypeScript
- HTML, CSS, SCSS, Less
- JSON, YAML, Markdown
- GraphQL, SQL, etc.
Installing Prettier
To introduce Prettier, run the following command:
npm install --save-dev prettier
Or, if you use Yarn:
yarn add -D prettier
Creating a configuration file
Create .prettierrc in the project root and define formatting rules.
{
"printWidth": 100,
"tabWidth": 2,
"semi": true,
"singleQuote": true
}
Details of each property
-
printWidth: 100- Description: Specifies the maximum number of characters per line.
- Effect: When a line exceeds 100 characters, it is automatically wrapped. Prevents code from becoming too wide horizontally.
- Default value: 80
-
tabWidth: 2- Description: Specifies the width of spaces for indentation.
- Effect: Uses 2 spaces for indentation. Compared to 4 spaces, code becomes more compact and visibility improves.
- Default value: 2
-
semi: true- Description: Specifies whether to add
;(semicolons) at the end of statements. - Effect:
true→ Always add semicolons.false→ Omit semicolons. - Default value: true
- Note: In JavaScript, semicolons can be omitted, but they are often recommended to prevent unintended interpretation of code.
- Description: Specifies whether to add
-
singleQuote: true- Description: Specifies whether to wrap strings with ' (single quotes) or " (double quotes).
- Effect:
true→ Use single quotes '.false→ Use double quotes ". - Default value: false (double quotes)
- Notes
- The default JSON format in JavaScript uses double quotes, so double quotes are more common when dealing with JSON files.
- However, in JavaScript and TypeScript, many people prefer single quotes because they are easier to type.
Avoiding conflicts between ESLint and Prettier
ESLint is a static analysis tool for JavaScript/TypeScript that improves code quality by pointing out syntax mistakes and code that violates best practices.
Prettier is a tool for unifying code formatting and preventing style inconsistencies.
When using these two together, some ESLint rules (e.g., indentation or quote style) can conflict with Prettier’s automatic formatting. To solve this, integrate Prettier into ESLint as follows:
npm install --save-dev eslint-config-prettier eslint-plugin-prettier
Roles of the packages
-
eslint-config-prettier- A configuration that disables ESLint’s formatting-related rules (e.g., indent, quotes) and delegates them to Prettier.
- This prevents ESLint from conflicting with Prettier’s rules.
-
eslint-plugin-prettier- A plugin that runs Prettier inside ESLint and reports formatting violations as ESLint errors.
Edit .eslintrc.js to integrate Prettier into ESLint.
module.exports = {
extends: ["eslint:recommended", "plugin:react/recommended", "prettier"],
plugins: ["prettier"],
rules: {
"prettier/prettier": "error"
}
};
Key points of the configuration
- Add
"prettier"to"extends"to disable ESLint’s formatting-related rules and let Prettier handle them. - Add
"prettier"to"plugins"so that Prettier’s formatting can be checked as ESLint rules. - Add
"prettier/prettier": "error"to"rules"so that Prettier formatting violations are detected as ESLint errors and prompt fixes.
Using Git Hooks for automatic application
Git Hooks are scripts that automatically run before or after specific Git operations (e.g., commit, push, merge).
By using them, you can apply ESLint and Prettier before commits and ensure code quality.
Introducing Husky and lint-staged
To easily manage Git Hooks, introduce the following tools:
-
Husky- A tool for managing Git hooks that can automatically run scripts at commit or push time. This enables improvements in code quality and standardization of commit rules.
- Easily apply hooks such as pre-commit and pre-push
- pre-push: Runs before pushing
-
lint-staged- A tool that applies
ESLintandPrettieronly to files that are being committed (i.e., staged files) - By applying
ESLint/Prettieronly to changed files instead of the entire project, it shortens execution time
- A tool that applies
Installing Husky and lint-staged
Introduce husky and lint-staged to automatically apply ESLint and Prettier before commits.
npm install --save-dev husky lint-staged
Add the following configuration to package.json:
"husky": {
"hooks": {
"pre-commit": "lint-staged"
}
},
"lint-staged": {
"*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}": [
"eslint --fix",
"prettier --write"
]
}
Configuration details
-
Huskyconfiguration- "pre-commit": "lint-staged"
- Run lint-staged before commits (pre-commit)
- This ensures that only files being committed are targeted
- "pre-commit": "lint-staged"
-
lint-stagedconfiguration"*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx}": Target JavaScript, JSX, TypeScript, and TSX files["eslint --fix", "prettier --write"]:- Use eslint --fix to automatically fix ESLint rule violations
- Use prettier --write to apply Prettier and format code
Enabling Husky
To apply Husky’s configuration, run the following command:
npx husky install
Or, if you use Yarn:
yarn husky install
Running this command creates a .husky directory, which will manage Git Hooks scripts.
Automatically fixing code style issues
Manually applying ESLint and Prettier
To apply ESLint to all files, run:
npx eslint . --fix
To apply Prettier, run:
npx prettier --write .
Adding to npm scripts
You can make them easy to run by adding scripts to package.json:
"scripts": {
"lint": "eslint . --fix",
"format": "prettier --write ."
}
Standardizing commit message format with Husky
By using Husky, you can leverage Git hooks to run specific scripts before commits or pushes. It is common to combine it with commitlint to standardize commit message formats.
Installing and configuring Commitlint
npm install --save-dev @commitlint/{config-conventional,cli}
This installs the following packages:
@commitlint/config-conventional: Defines common commit message rules@commitlint/cli: CLI tool that checks commit messages
Configure rules in commitlint.config.js:
module.exports = {
extends: ['@commitlint/config-conventional']
};
For example, the following commit messages are allowed:
feat: add new feature
fix: fix bug
docs: update documentation
style: fix code formatting (no functional changes)
Configuring commitlint in Husky
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg 'npx --no-install commitlint --edit "$1"'
Running this command creates a .husky/commit-msg file and adds a script that runs commitlint checks.
How it works
- The
commit-msghook runs npx --no-install commitlint --edit "$1"checks the commit message- If it violates the rules, an error occurs and the commit is rejected
Customizing commit messages
By default, @commitlint/config-conventional recommends the following format:
<type>: <message>
Main types:
- feat (new feature)
- fix (bug fix)
- docs (documentation changes)
- style (formatting changes, no impact on code behavior)
- refactor (code refactoring, no functional changes)
- test (add or update tests)
- chore (build or tooling-related changes)
You can customize as needed.
For example, to limit the maximum length of commit messages:
module.exports = {
extends: ['@commitlint/config-conventional'],
rules: {
'header-max-length': [2, 'always', 72]
}
};
Integrating Lint and Prettier into the CI/CD pipeline
By running Lint (ESLint) and code formatting (Prettier) in the CI/CD pipeline, you gain the following benefits:
-
Improved code quality
- Lint makes it easier to detect code inconsistencies and errors.
- Prettier unifies code formatting and improves readability.
-
Reduced effort for developers
- No need to run Lint manually.
- Checks are automatically run on pull requests (PRs), reducing the burden on reviewers.
-
Maintaining quality through continuous integration (CI)
- If Lint or formatting checks fail for a PR, you can prevent merging and keep the codebase healthy.
Running ESLint and Prettier with GitHub Actions
This section explains in detail how to automate Lint and formatting checks using GitHub Actions.
Create .github/workflows/lint.yml and add the following configuration:
name: Lint and Format Check
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: 18
- run: npm install
- run: npm run lint
- run: npm run format:check
To make this workflow work, you need to define appropriate scripts in package.json.
{
"scripts": {
"lint": "eslint . --ext .js,.jsx,.ts,.tsx",
"format": "prettier --write \"src/**/*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx,json,md}\"",
"format:check": "prettier --check \"src/**/*.{js,jsx,ts,tsx,json,md}\""
},
"devDependencies": {
"eslint": "^8.0.0",
"prettier": "^3.0.0"
}
}
lint→ Apply ESLint to the entire projectformat→ Apply Prettier to format codeformat:check→ Run a check for code formatting (does not modify code)
How it works
-
Push code to GitHub or create a PR
on: [push, pull_request]triggers the workflow automatically when code is pushed to GitHub or a PR is created. -
Run the job on an Ubuntu environment
runs-on: ubuntu-latestruns the job on an Ubuntu environment. -
Fetch repository code
Useactions/checkout@v3to check out the code into the CI environment. -
Set up Node.js environment
Install Node.js 18 withactions/setup-node@v3. -
Install dependencies
Runnpm installto install required packages based on package.json. -
Run Lint check
Run ESLint withnpm run lint. -
Run Prettier format check
Runnpm run format:checkto verify that code formatting is correct.
Extra
To automatically fix Lint and formatting errors and reflect them in the PR, you can add a workflow that runs prettier --write in GitHub Actions and commits the changes.
name: Lint and Format Auto Fix
on:
pull_request:
jobs:
lint-fix:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: 18
- run: npm install
- run: npm run lint --fix
- run: npm run format
- name: Commit and push changes
run: |
git config --global user.name "github-actions[bot]"
git config --global user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
git add .
git commit -m "chore: apply auto lint and format fixes" || echo "No changes to commit"
git push
- Run ESLint and Prettier to automatically fix code.
- Commit the fixed code to the PR as the GitHub Actions bot user.
- Adding
|| echo "No changes to commit"aftergit commit -mprevents errors when there are no changes.
Mechanisms for visualizing code quality
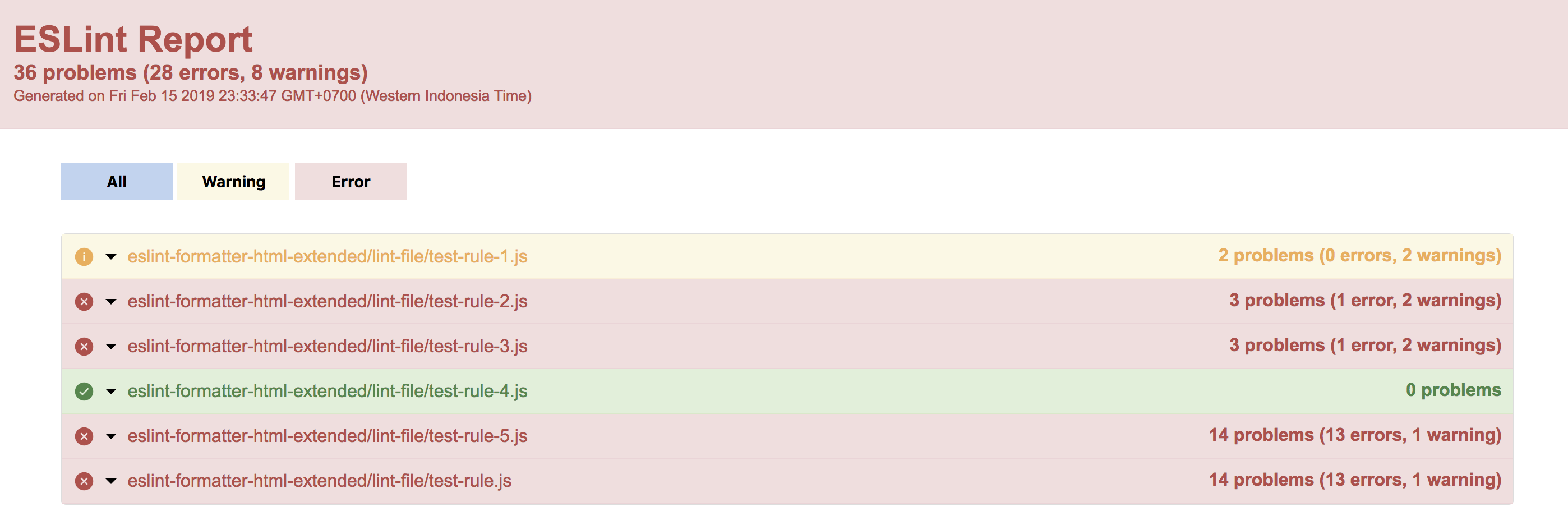
Generating Lint reports
ESLint is a static analysis tool used to improve the quality of JavaScript/TypeScript code. By using eslint-formatter-html, you can output ESLint results in HTML format and visually inspect them in a browser.
Installing the package
npm install --save-dev eslint-formatter-html
Generating a Lint report
npm run lint -- --format html > lint-report.html
Reference:
npm run lintchecks code based on the project’s ESLint configuration.--format htmloutputs in HTML format.> lint-report.htmlsaves the output to a lint-report.html file.
How to use it
- Integrate into the CI/CD pipeline to visualize Lint errors.
- Share the report during code reviews as a guide for fixes.
- Check locally and view detailed error information in the browser.
Quality management using SonarQube
SonarQube is a tool that analyzes code quality and evaluates bugs, security vulnerabilities, code duplication, and maintainability.
Introducing SonarQube
docker run -d --name sonar -p 9000:9000 sonarqube
docker run -d: Run the container in the background.--name sonar: Create a container named sonar.-p 9000:9000: Map local port 9000 to SonarQube’s port 9000.sonarqube: Use the official SonarQube Docker image.
Analyzing a project
sonar-scanner -Dsonar.projectKey=my_project -Dsonar.sources=src -Dsonar.host.url=http://localhost:9000
sonar-scanner: Command to have SonarQube analyze your code.-Dsonar.projectKey=my_project: Specify the project key (configured in the SonarQube admin screen).-Dsonar.sources=src: Analyze code in the src directory.-Dsonar.host.url=http://localhost:9000: Specify the SonarQube host URL.
How to use it
- Integrate into CI/CD: Continuously monitor code quality and raise alerts when issues occur.
- Visualize technical debt: Identify areas of code that need refactoring.
- Improve team development quality: Use it as an indicator for quality improvement through static analysis.
Summary
This article explained the following initiatives in detail:
- Define ESLint rules that match your development team’s coding style and configure the project optimally
- Introduce Prettier to automatically unify code formatting
- Use Git hooks to automatically run ESLint and Prettier before commits
- Automatically fix code style issues
- Create documentation for configuration and usage
- Use Husky to standardize commit message formats
- Integrate Lint and Prettier into the CI/CD pipeline
- Visualize code quality as reports and build a mechanism for the entire team to track quality improvement progress
By doing this, it becomes easier to standardize code style within the development team and reduce the burden of code reviews.
If you are considering introducing these tools, give them a try.
Questions about this article 📝
If you have any questions or feedback about the content, please feel free to contact us.Go to inquiry form
Related Articles
Complete Guide to Web Accessibility: From Automated Testing with Lighthouse / axe and Defining WCAG Criteria to Keyboard Operation and Screen Reader Support
2023/11/21Introduction to Automating Development Work: A Complete Guide to ETL (Python), Bots (Slack/Discord), CI/CD (GitHub Actions), and Monitoring (Sentry/Datadog)
2024/02/12CI/CD Strategies to Accelerate and Automate Your Development Flow: Leveraging Caching, Parallel Execution, and AI Reviews
2024/03/12Strengthening Dependency Security: Best Practices for Vulnerability Scanning, Automatic Updates, and OSS License Management
2024/01/29Building and Operating a Design System Using Chakra UI, ShadCN, and Material UI
2024/03/12How to Easily Build a Web API with Express and MongoDB [TypeScript Compatible]
2024/12/09Express (+ TypeScript) Beginner’s Guide: How to Quickly Build Web Applications
2024/12/07Complete Guide to Refactoring React: Improve Your Code with Modularization, Render Optimization, and Design Patterns
2025/01/13